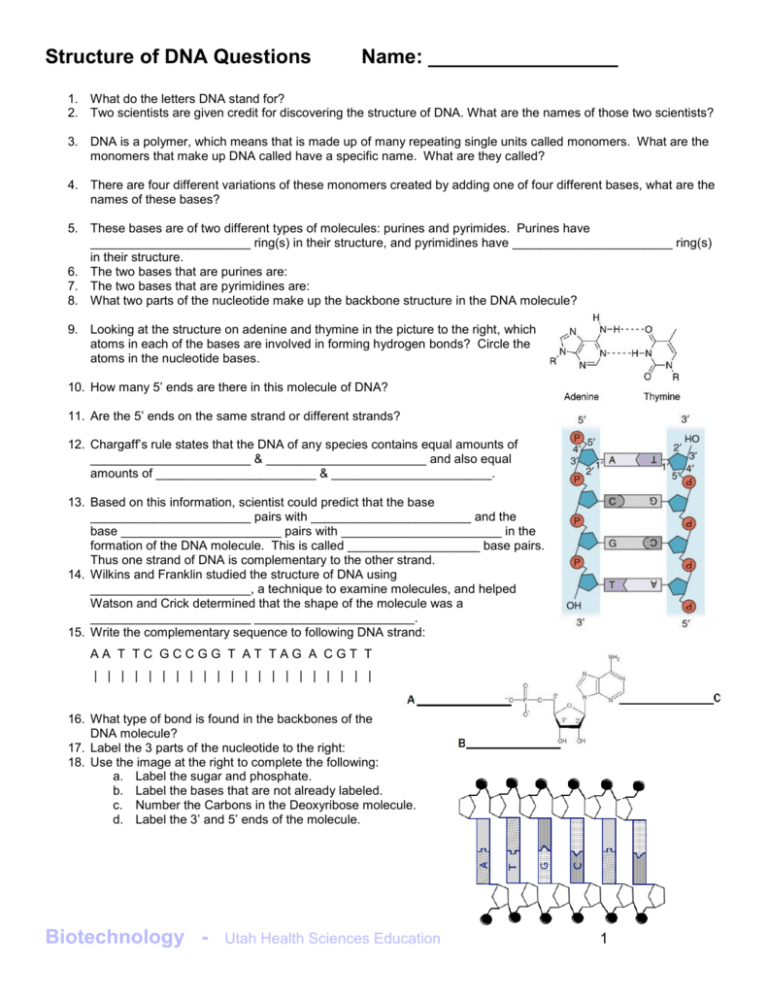
42 parts of a nucleotide labeled
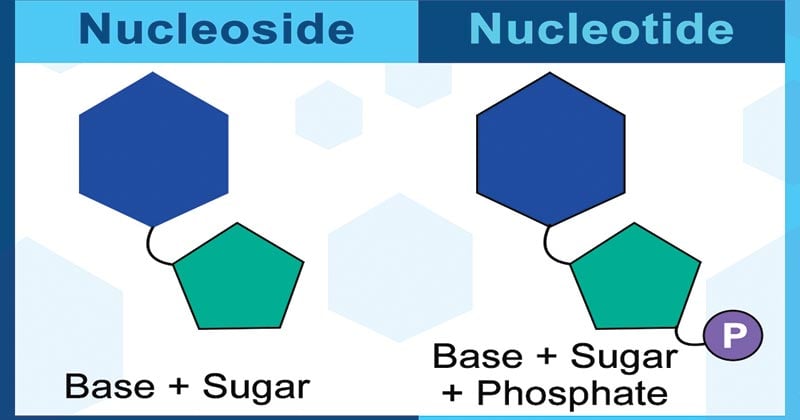
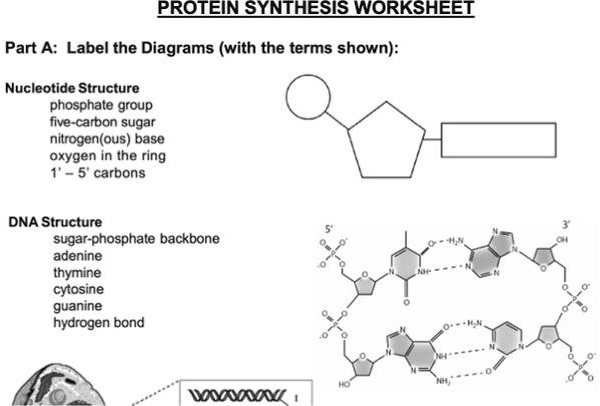
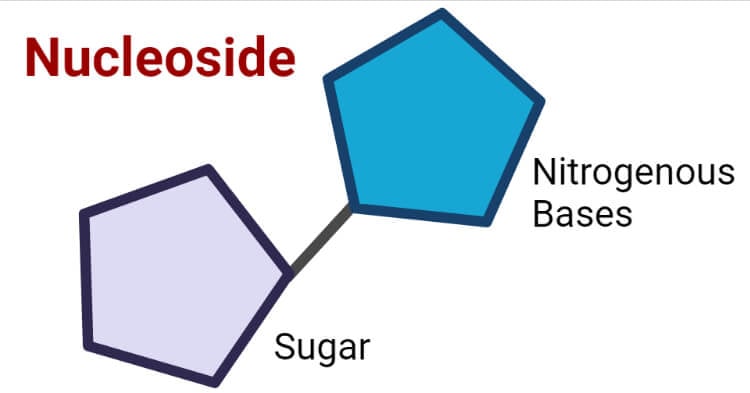
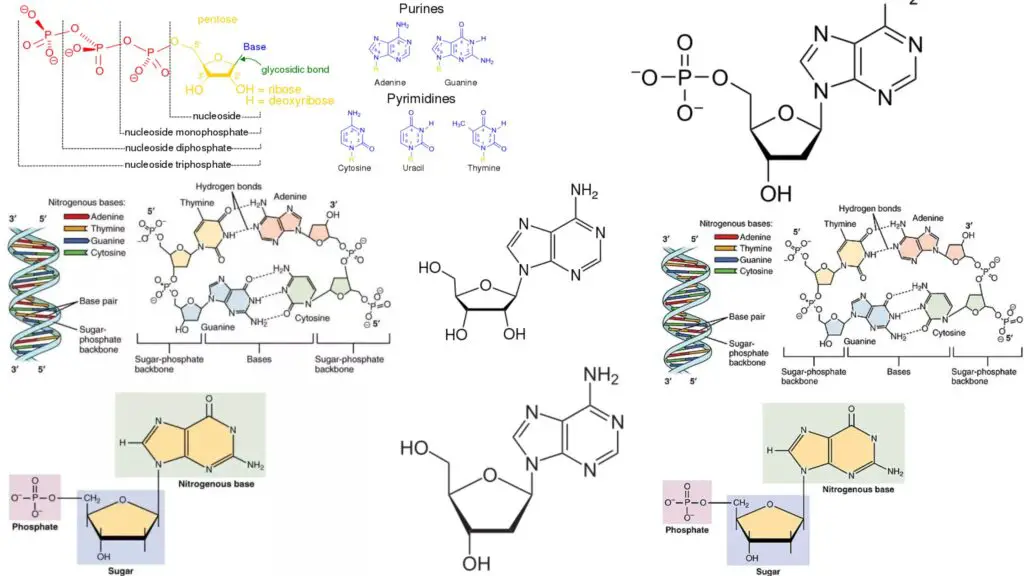
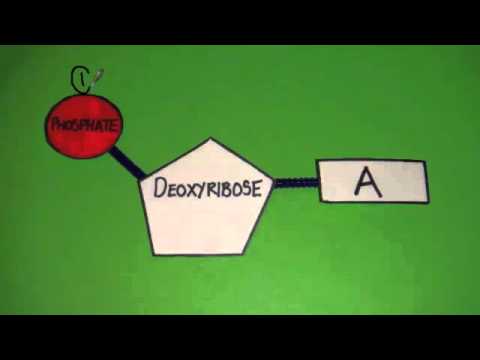
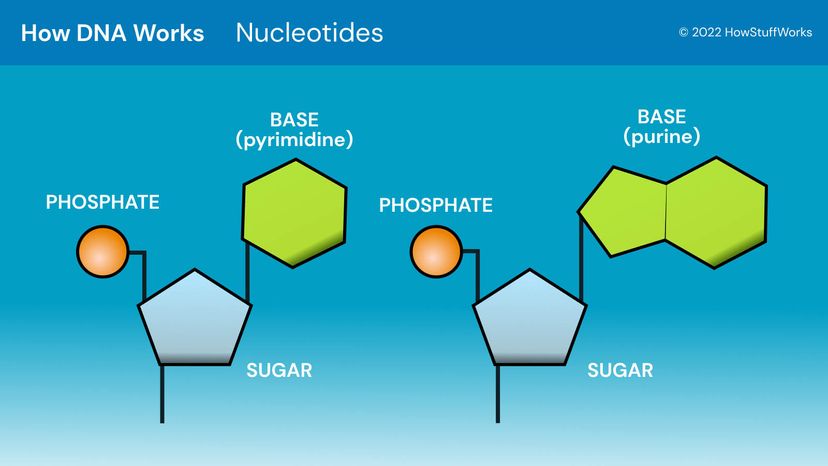
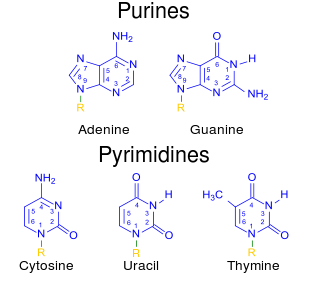
Describe the Parts of a Nucleotide | Biology - Biology Discussion A nucleotide is composed of a nitrogenous base, pentose sugar and a phosphate group. Part # 1. A Nitrogenous Base: It is a nitrogen-containing organic molecule having similar physical properties of a base. There are two types of nitrogenous bases: ADVERTISEMENTS: (a) Purines Adenine and Guanine. (b) Pyrimidines Cytosine, Uracil and Thymine. 3 Parts of a Nucleotide and How They Are Connected - ThoughtCo Nucleotides in DNA and RNA Both deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are made up of nucleotides which consist of three parts: Nitrogenous Base Purines and pyrimidines are the two categories of nitrogenous bases. Adenine and guanine are purines. Cytosine, thymine, and uracil are pyrimidines.
› tools › primer-blastPrimer designing tool - National Center for Biotechnology ... Enter a list of space separated nucleotide positions. This requires that the left or the right primers to span a junction that is just 3' of any such positions. For example, entering "50 100" would mean that the left or the right primers must span the junction between nucleotide position 50 and 51 or the junction between position 100 and 101 ...
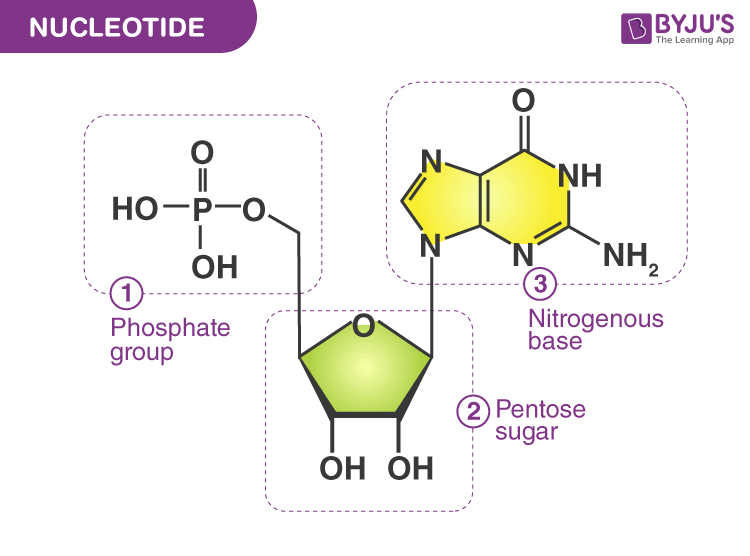
Parts of a nucleotide labeled
What are the three parts of a nucleotide? Flashcards | Quizlet What are the three parts of a nucleotide? Phospate, sugur, nitrogen base Nucleotide basic unit surgery in DNA deoxylibonuelic hydrogen bonds hold DNA together covalent bond is sharing of electrons ionic is the attraction between 2 ions 4 nitrogen bases cytosine, thymine, adenine, guanine DNA is a polymer › books › NBK21117Sequencing Genomes - Genomes - NCBI Bookshelf Chain termination sequencing in outline. The starting material for a chain termination sequencing experiment is a preparation of identical single-stranded DNA molecules. The first step is to anneal a short oligonucleotide to the same position on each molecule, this oligonucleotide subsequently acting as the primer for synthesis of a new DNA strand that is complementary to the template (Figure ... Nucleotide Structure, Parts & Function | What is a Nucleotide ... A nucleotide is the monomer (building block) of nucleic acids. Nucleotides contain three main parts: a nitrogenous base, a sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and one or more phosphate groups....
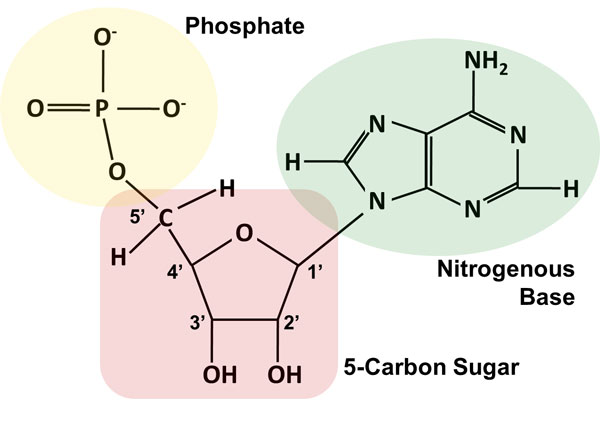
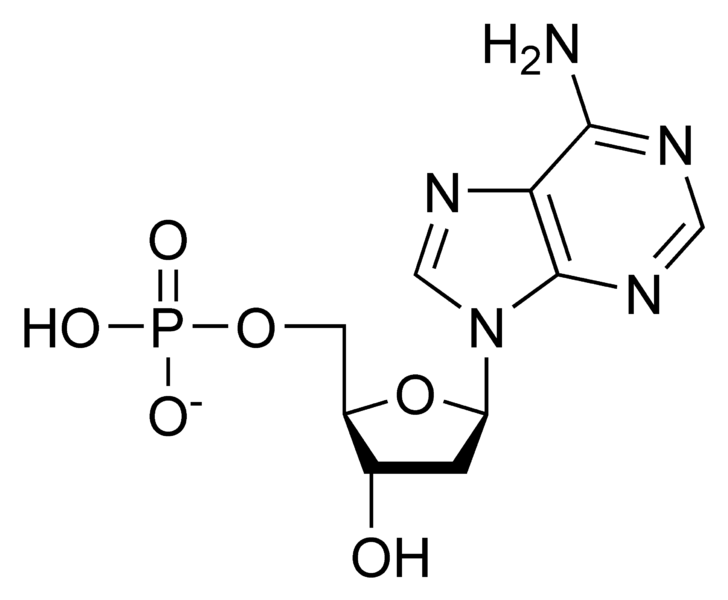
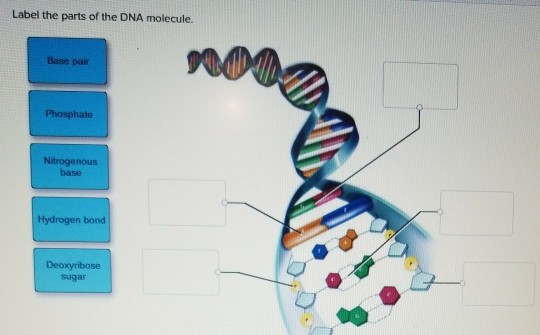
Parts of a nucleotide labeled. Use the drop-down menus to label the parts of a nucleotide. - Brainly.com A nucleotide is a molecule composed of a pentose sugar (ribose in RNA and deoxyribose in DNA), a nitrogenous base, and a phosphate group. In DNA, there are four types of nucleotides that contain four different classes of nitrogen bases: Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine and Thymine. In RNA, Thymine bases are replaced by Uracil bases. Nucleotide - Genome A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acids (RNA and DNA). A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA) attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base. The bases used in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T). Cell signaling - Wikipedia In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) or cell communication is the ability of a cell to receive, process, and transmit signals with its environment and with itself. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellular life in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Signals that originate from outside a cell (or extracellular signals) can be physical agents like mechanical ... Nucleotide Structure: DNA Diagram - Science Trends Nucleotides are made out of elements like nitrogen and carbon with a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar component, and a group of phosphates. However, there are some important differences between RNA nucleotides and DNA nucleotides. The nitrogenous bases come in one of two different forms - they are either a pyrimidine or a purine.
How do you draw a nucleotide and label its three basic parts? How do you draw a nucleotide and label its three basic parts? | Socratic How do you draw a nucleotide and label its three basic parts? Biology Molecular Biology Basics Nucleic Acids 1 Answer Maxwell Jul 19, 2017 See below Explanation: The above structure is a nucleotide. It consists of a: phosphate group 5-carbon sugar, and nitrogenous base. Join LiveJournal Password requirements: 6 to 30 characters long; ASCII characters only (characters found on a standard US keyboard); must contain at least 4 different symbols; Lifestyle | Daily Life | News | The Sydney Morning Herald The latest Lifestyle | Daily Life news, tips, opinion and advice from The Sydney Morning Herald covering life and relationships, beauty, fashion, health & wellbeing Nucleotides | BioNinja Each nucleotide is comprised of three principal components: 5-carbon pentose sugar (pentagon) Phosphate group (circle) Nitrogenous base (rectangle) Both the phosphate group and nitrogenous base are attached to the central pentose sugar The nitrogenous base is attached to the 1'- carbon atom (right point)
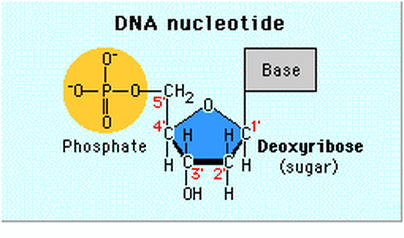
Name the 3 parts of a Nucleotide? - Answers A nucleotide has three parts: a sugar, a base, and a phosphate group, which contains phosphorus and oxygen atoms. its attached by DNA, RNA, and ATP. The Structure of DNA - University of Arizona The boxed area at the lower left encloses one nucleotide. Each nucleotide is itself make of three subunits: A five carbon sugar called deoxyribose (Labeled S) A phosphate group (a phosphorous atom surrounded by four oxygen atoms.) (Labeled P) And one of four nitrogen-containing molecules called nucleotides . (Labeled A, T, C, or G) Nucleotide - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Nucleotides make long polymers, as shown in the left side of Fig. 7.7, which is labeled from 5′ to 3′.This polymer makes a helix with a corresponding right side helix. Finally, the two polymers make the double helix as shown in Fig. 7.7.Two ends of phosphoric acid and deoxyribose are called the 5′ end and 3′ end, respectively. › web › offices2422-Nucleotide and/or Amino Acid Sequence Disclosures in ... Jun 25, 2020 · 2422.01 Nucleotide and/or Amino Acids Disclosures Requiring a Sequence Listing [R-10.2019] I. LENGTH THRESHOLDS. 37 CFR 1.821(a) presents a definition for "nucleotide and/or amino acid sequences." This definition sets forth limits, in terms of numbers of amino acids and/or numbers of nucleotides, at or above which compliance with the sequence ...
What are the three parts of a nucleotide? - Toppr Ask How do you draw a nucleotide and label its three basic parts? Medium. View solution > What are three parts of a nucleus? Medium. View solution > Three samples of a radioactive substance have activity in a ratio 2:5:7 , then after two half lives the ratio of their activities will be: Hard.
Nucleotide - Definition, Structure (3 Parts), Examples & Function A nucleotide is an organic molecule that is the building block of DNA and RNA. They also have functions related to cell signaling, metabolism, and enzyme reactions. A nucleotide is made up of three parts: a phosphate group, a 5-carbon sugar, and a nitrogenous base. The four nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine.
Primer designing tool - National Center for Biotechnology … Enter a list of space separated nucleotide positions. This requires that the left or the right primers to span a junction that is just 3' of any such positions. For example, entering "50 100" would mean that the left or the right primers must span the junction between nucleotide position 50 and 51 or the junction between position 100 and 101 (counting from 5' to 3').
Nucleotides and Bases - Genetics Generation Nucleotide Structure Courtesy of the National Human Genome Research Institute. Nucleotides. A nucleotide is the basic structural unit and building block for DNA. These building blocks are hooked together to form a chain of DNA. A nucleotide is composed of 3 parts: * five-sided sugar * phosphate group * nitrogenous base (nitrogen containing)
What Are the Three Parts of a Nucleotide? - Science Notes and Projects The three parts of a nucleotide are the base, the sugar, and the phosphate. Nucleotides are the building blocks of DNA (2′-deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid). DNA and RNA code genetic information, transport energy throughout cells, and serve as cell signaling molecules.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Dominant_whiteDominant white - Wikipedia The W2 allele is linked to a single nucleotide polymorphism (c.1960G>A), a missense mutation where a glycine is replaced with arginine (p.G654R) in the protein kinase domain, located on exon 17. W3 is found in Arabian horses descended from R Khasper, a near-white stallion born in 1996. Neither of his parents were white, and the causative ...
Nucleotide: Structure, Examples and Function - BYJUS Nucleotides are the fundamental blocks of nucleic acids - DNA and RNA. It comprises sugar molecule attached to a phosphate group and a base which contains nitrogen. In DNA, the bases used are adenine, cytosine, thymine and guanine. Test your Knowledge on Nucleotide! Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs.
Explanation of 3 Parts of a Nucleotide and Nucleotide Examples - HoneyReads Within the 3 parts of a nucleotide, there are five types of nucleotide bases which are: Adenine (A), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G), Thymine (T) and Uracil (U). When they are combined with sugar, they form nucleotide adenosine, cytidine, guanosine, thymidine, and uridine. 1. Adenine
608-Disclosure - United States Patent and Trademark Office 608 Disclosure [R-11.2013] To obtain a valid patent, a patent application as filed must contain a full and clear disclosure of the invention in the manner prescribed by 35 U.S.C. 112(a).The requirement for an adequate disclosure ensures that the public receives something in return for the exclusionary rights that are granted to the inventor by a patent.
How do you draw a nucleotide and label its three basic parts? - Toppr Ask Solution. Verified by Toppr. The above structure is a nucleotide. It consists of a: phosphate group. 5-carbon sugar, and. nitrogenous base. Was this answer helpful?
› Tools › msaClustal Omega < Multiple Sequence Alignment < EMBL-EBI Clustal Omega is a multiple sequence alignment program. It produces biologically meaningful multiple sequence alignments of divergent sequences. Evolutionary relationships can be seen via viewing Cladograms or Phylograms.
Clustal Omega < Multiple Sequence Alignment < EMBL-EBI Clustal Omega is a new multiple sequence alignment program that uses seeded guide trees and HMM profile-profile techniques to generate alignments between three or more sequences. For the alignment of two sequences please instead use our pairwise sequence alignment tools. Important note: This tool can align up to 4000 sequences or a maximum file size of 4 MB.
Nucleotides | Types, Examples, Functions & Classification Three molecular structures join to form a nucleotide. These are: A Pentose Sugar A Nitrogenous Base One or more phosphate groups Let us have some brief discussion on these constituents of nucleotides. Pentose Sugar A pentose sugar is a monosaccharide having five carbon atoms. It occupies the central position in the structure of a nucleotide.
Exam 4 61. Draw a nucleotide and label all parts. (see lecture notes) Draw a nucleotide and label all parts. (see lecture notes) + − Learn Test Match Created by Tryton_Taylor Plus 61. Draw a nucleotide and label all parts. (see lecture notes) Terms in this set (3) phosphate ... nitrogen base ... 5 carbon sugar ... Sets found in the same folder Biology Exam 4 Study Guide 221 terms Tryton_Taylor Plus 7.
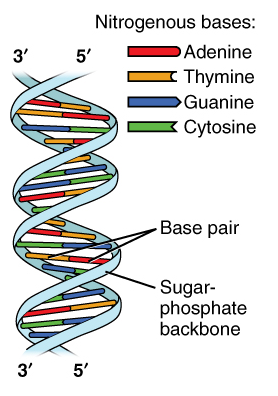
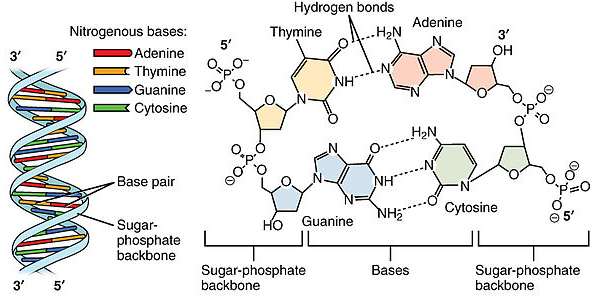
What are the Three Parts of a Nucleotide? | Albert.io Nucleotides are made up of 3 parts. The first is a distinct nitrogenous base, which is adenine, cytosine, guanine or thymine. In RNA, thymine is replaced by uracil. These nitrogenous bases are either purines or pyrimidines. Base pairs are formed when adenine forms a hydrogen bond with thymine, or cytosine forms a hydrogen bond with guanine.
Parts of the dna - LORECENTRAL A deoxyribose , which corresponds to a sugar molecule.; A phosphate group. A base : where there are four bases or nitrogen compounds, which are: guanine, adenine, cytosine and thymine. Chromosome Chromosome. These structures are located right in the nucleus or center of the cells. They are responsible for carrying the fragments of great length of DNA, at the same time it has proteins that ...
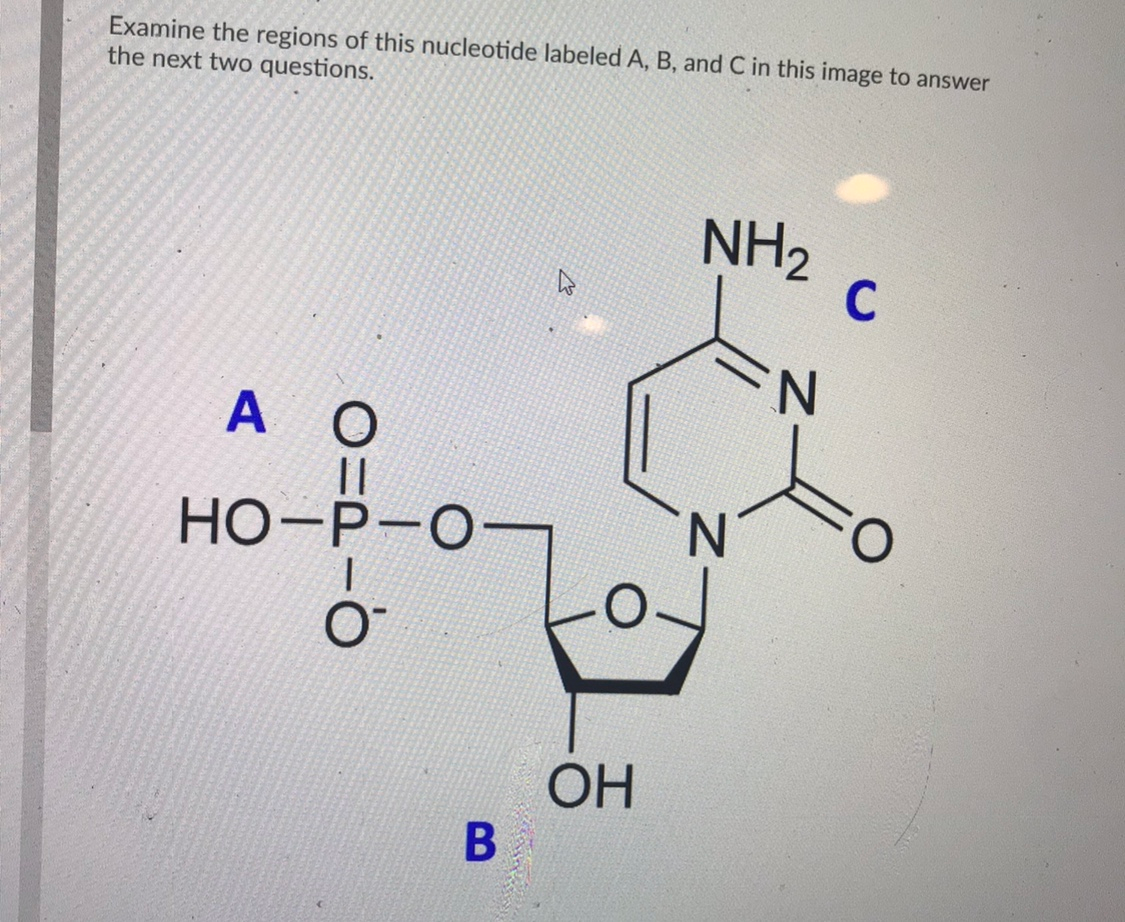
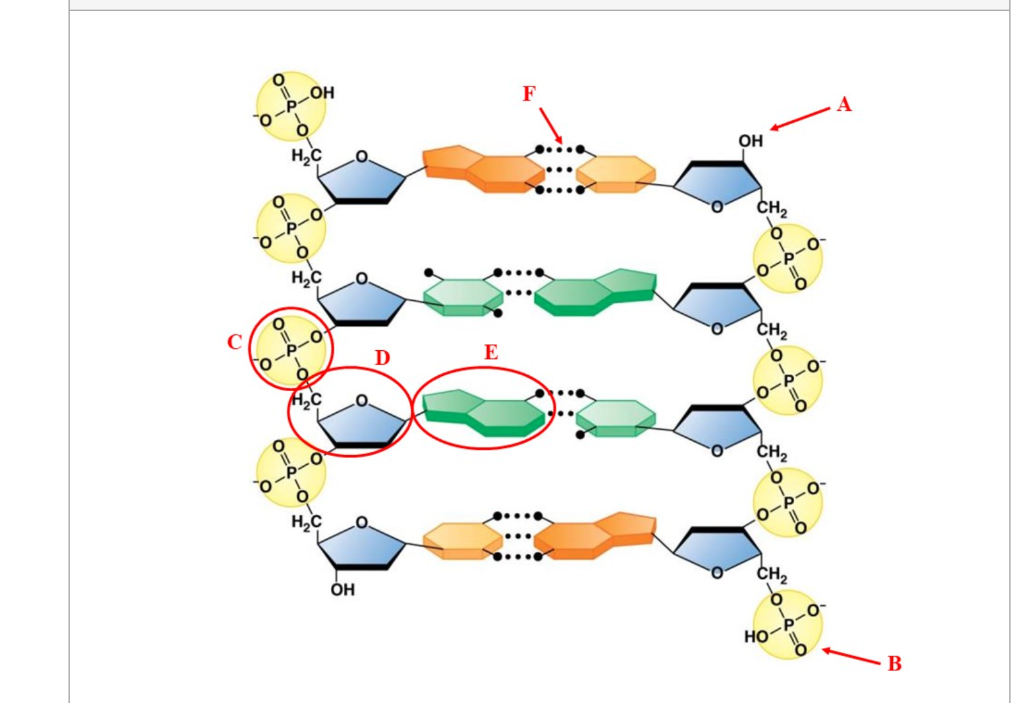
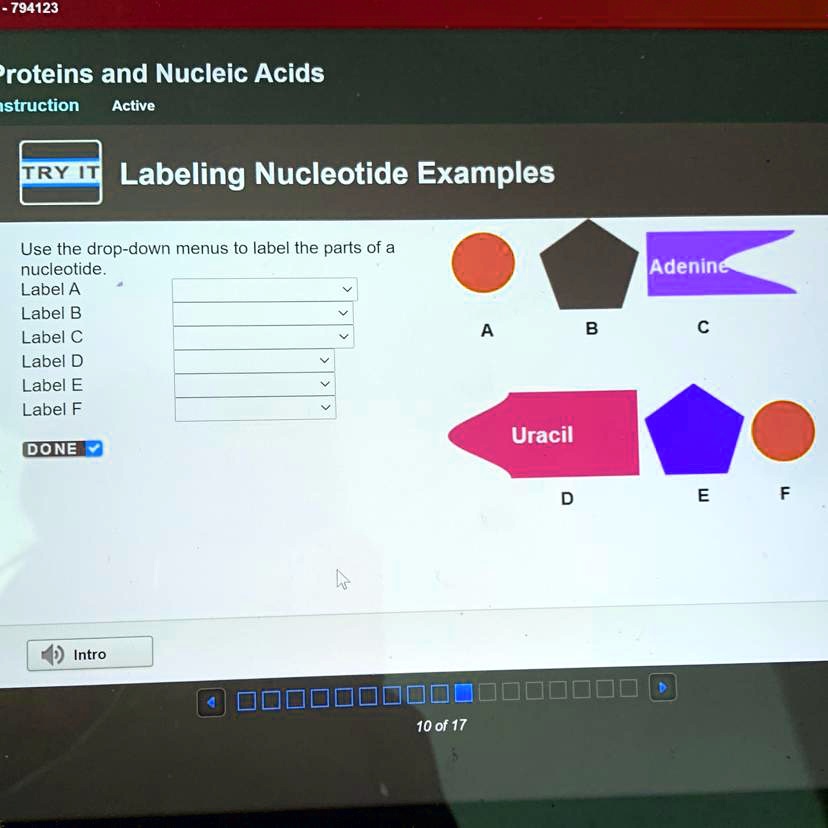
Use the drop-down menus to label the parts of a nucleotide. Label A ... Use the drop-down menus to label the parts of a nucleotide. Label A 2 See answers Advertisement hjennings Answer: A- phosphate group B- 5-carbon sugar C- nitrogenous base (adenine is a purine, just in case) D- nitrogenous base (uracil is only found in RNA) E- 5-Carbon sugar F- phosphate group Explanation: Advertisement sebastiando0912 Answer:
Allergy - Wiley Online Library Parts of the Manuscript. The manuscript should be submitted in separate files: ... Changes made on Figures and Tables should be clearly visible and provided as separate files labeled as 'Figure x Marked' and 'Table x Marked'. ... Nucleotide sequence data can be submitted in electronic form to any of the three major collaborative databases: ...
Gene expression - Wikipedia Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, protein or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype, as the final effect.These products are often proteins, but in non-protein-coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) and small nuclear RNA (snRNA), the …
What is Nucleotide? Definition, Properties, Components & Functions ... A nucleotide is a compound, which can form a polynucleotide chain by the union of nitrogenous bases and sugar-phosphate group. Monomers of nucleotide units are connected via a covalent phosphodiester bond. Nitrogenous bases, i.e. purines and pyrimidine, are attached via weak hydrogen bonds. The bases link with a deoxyribose pentose sugar via an ...
Nucleotide - Wikipedia Nucleotides are composed of three subunit molecules: a nucleobase, a five-carbon sugar ( ribose or deoxyribose ), and a phosphate group consisting of one to three phosphates. The four nucleobases in DNA are guanine, adenine, cytosine and thymine; in RNA, uracil is used in place of thymine.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Electron_transport_chainElectron transport chain - Wikipedia An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes and other molecules that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) and couples this electron transfer with the transfer of protons (H + ions) across a membrane.
Patent Public Search | USPTO Welcome to Patent Public Search. The Patent Public Search tool is a new web-based patent search application that will replace internal legacy search tools PubEast and PubWest and external legacy search tools PatFT and AppFT.
› mgihome › nomenMGI-Guidelines for Nomenclature of Genes, Genetic Markers ... 3.2.3 Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) Polymorphisms defined by SNPs may occur within or outside of a protein coding sequence. If the SNP occurs within a gene, the SNP allele can be designated based on its dbSNP_ID, followed by a hyphen and the specific nucleotide. Examples:
Draw And Label The Three Parts Of A Nucleotide A nucleotide is the building block or monomer of a nucleic acid chian the three parts of a nucleotide are. Draw and label the three parts of a nucleotide. Diagram and label the two types of nitrogenous bases. It consists of a. A phosphate group a sugar and a base. Small sections of a DNA molecule that determine genetic traits are called of a ...
Electron transport chain - Wikipedia Mitochondrial electron transport chains. Most eukaryotic cells have mitochondria, which produce ATP from reactions of oxygen with products of the citric acid cycle, fatty acid metabolism, and amino acid metabolism.At the inner mitochondrial membrane, electrons from NADH and FADH 2 pass through the electron transport chain to oxygen, which provides the energy driving the …
The 5 Kinds of Nucleotides - ThoughtCo The five bases are adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine, and uracil, which have the symbols A, G, C, T, and U, respectively. The name of the base is generally used as the name of the nucleotide, although this is technically incorrect. The bases combine with the sugar to make the nucleotides adenosine, guanosine, cytidine, thymidine, and uridine.
Methods for Labeling Nucleic Acids - Thermo Fisher Scientific Summary of nucleic acid labeling methods. 1. 5′ end-labeled primers can be used with this method in order to add a 5′ modification to a DNA probe. 2. Modified nucleotides can be added to the 3′ recessed-end of double-stranded DNA during fill-in reactions. 3.
Solved Label the different parts of the nucleotide below, A - Chegg Expert Answer. 100% (1 rating) Transcribed image text: Label the different parts of the nucleotide below, A 5.phosphoryl group NH2 Adenine nucleotide base N. N Ribose sugar -20₃Po- N N 2hydroxy! group OH OHO.
Nucleotide Structure, Parts & Function | What is a Nucleotide ... A nucleotide is the monomer (building block) of nucleic acids. Nucleotides contain three main parts: a nitrogenous base, a sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and one or more phosphate groups....
› books › NBK21117Sequencing Genomes - Genomes - NCBI Bookshelf Chain termination sequencing in outline. The starting material for a chain termination sequencing experiment is a preparation of identical single-stranded DNA molecules. The first step is to anneal a short oligonucleotide to the same position on each molecule, this oligonucleotide subsequently acting as the primer for synthesis of a new DNA strand that is complementary to the template (Figure ...
What are the three parts of a nucleotide? Flashcards | Quizlet What are the three parts of a nucleotide? Phospate, sugur, nitrogen base Nucleotide basic unit surgery in DNA deoxylibonuelic hydrogen bonds hold DNA together covalent bond is sharing of electrons ionic is the attraction between 2 ions 4 nitrogen bases cytosine, thymine, adenine, guanine DNA is a polymer


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-are-the-parts-of-nucleotide-606385-FINAL-5b76fa94c9e77c0025543061.png)






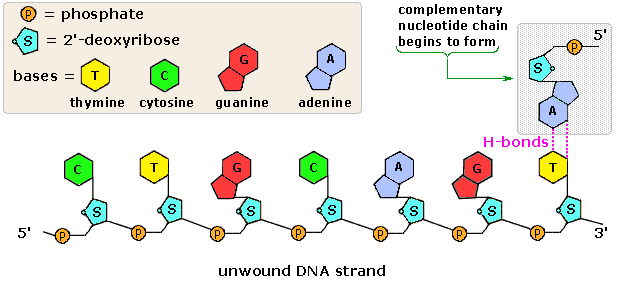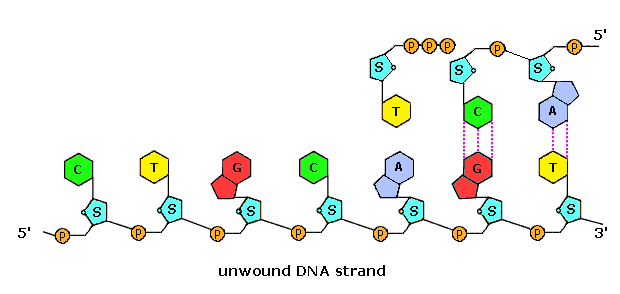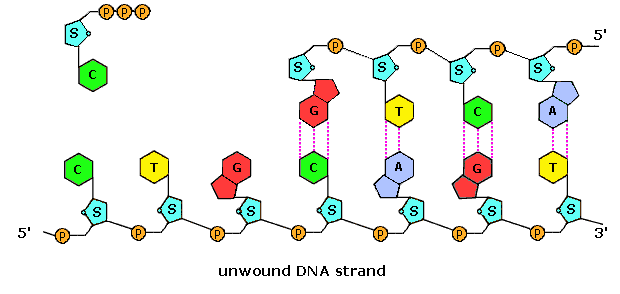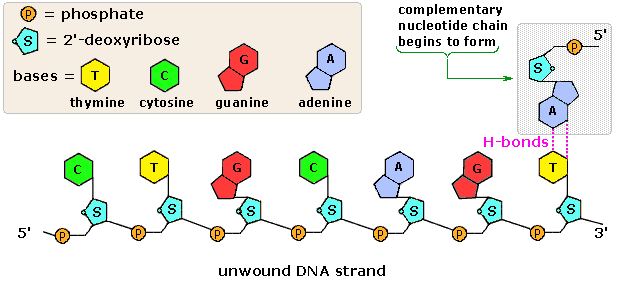










Post a Comment for "42 parts of a nucleotide labeled"